Breast Cancer in Males: What to Know
Males have a small amount of breast tissue and can get breast cancer. Breast cancer is a malignant growth of tissue (tumor) in the breast.
Unlike benign tumors, which aren't cancer, malignant tumors are cancer and can spread to other parts of the body.
What are the causes?
The cause of male breast cancer is not known.
What increases the risk?
These factors may make you more likely to develop breast cancer.- Age. Most cases of male breast cancer occur in people who are in their 60s or 70s.
- Having a family history of breast cancer, or having the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
- Having a history of radiation exposure.
- Having other medical conditions, such as:
- A genetic disorder called Klinefelter syndrome.
- Scarring on the liver.
- Certain problems that affect the testicles.
- Taking medicines that contain estrogen.
- Being very overweight (obese).
What are the signs or symptoms?
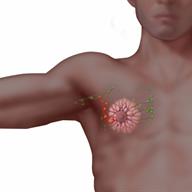 Symptoms of breast cancer include:
Symptoms of breast cancer include:- A painless lump in the breast.
- Changes in the size or shape of your breast.
- Breast skin changes, such as puckering or dimpling that looks like an orange peel.
- Sores on the skin.
- Nipple abnormalities, such as scaling, crustiness, redness, or pulling in.
- Nipple discharge that is bloody or clear.
How is this diagnosed?
Breast cancer may be diagnosed by:- Your medical history.
- A physical exam. Your health care provider will feel the tissue around your breast and under your arms.
- Taking a sample of any nipple discharge. The sample will be examined under a microscope.
- Imaging tests, such as breast X-rays (mammogram), ultrasound, or MRI.
- Taking a tissue sample from the breast. The sample will be examined to look for cancer cells.
- Taking a sample from the lymph nodes near the affected breast.
Your cancer will be staged after diagnosis to determine the size, location, and if it has spread in your body. This will help your cancer care team decide on a treatment that will work best for you. You may need to have more tests to determine the stage of your cancer.
How is this treated?
Depending on the type and stage, breast cancer may be treated with one or more of these therapies:- Surgery. The goal is to remove as much of the cancer as possible.
- This is done with a procedure to remove the whole breast and nipple. Some normal tissue surrounding this area may also be removed.
- This surgery may also involve removing lymph nodes in the area to be checked for cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy, which is the use of medicines to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy, which involves taking medicine to adjust the hormone levels in your body. You may take medicine to decrease your estrogen levels. This can help stop cancer cells from growing.
- Targeted therapy. There are medicines that are used to block the growth and the spread of cancer cells.
- These medicines target a specific part of the cancer cell and usually cause fewer side effects than chemotherapy.
- They may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy, which is the use of medicines to boost the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
- A combination of surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy may be needed to treat breast cancer.
Follow these instructions at home:
-
Take your medicines only as told.
- Eat a healthy diet. A healthy diet includes lots of fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and fiber.
- Make sure half your plate is filled with fruits or vegetables.
- Choose high-fiber foods such as whole-grain breads and cereals.
-
Consider joining a support group. This may help you cope with the stress of having breast cancer.
- Talk to your health care team about exercise and physical activity. The right exercise program can:
- Help prevent or reduce symptoms such as tiredness or depression.
- Improve overall health and survival rates.
Where to find more information
-
American Cancer Society: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer-in-men.html
-
National Cancer Institute: https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
Contact a health care provider if:
-
You have a sudden increase in pain.
-
You have any symptoms or changes that concern you.
-
You notice a new lump in either breast or under your arm.
-
You develop swelling in either arm or hand.
-
You lose weight without trying.
-
You have a fever.
-
You notice new tiredness or weakness.
Get help right away if:
-
You have chest pain.
-
You have trouble breathing.
-
Do not wait to see if the symptoms will go away.
-
Do not drive yourself to the hospital.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.

